What is the Network Security Key on a Macbook?
- 0
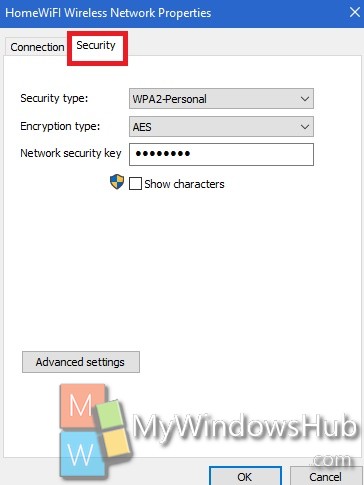
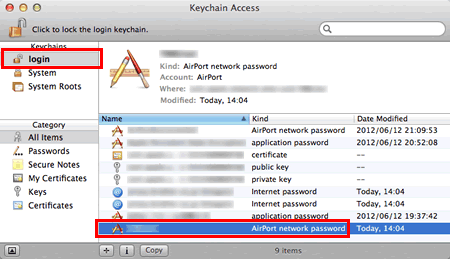
If you’re a Macbook user, you’ve probably wondered: What is the network security key? Well, this is a secret that can only be found on a Macbook. You’ll find it somewhere inside your device’s settings, but how do you find it? The best place to find it is inside your device itself. In this article, we’ll discuss how to find it and what to do when you’re unable to find it.
WPA2 uses AES encryption
The WPA2 standard uses AES encryption to secure internet data and prevent unauthorized access. A complex string of randomized letters and numbers protects WPA2-protected networks, making them harder to hack. However, it is easy to forget your network security key, making your data vulnerable to intruders. To avoid this, always remember your key. And never use your network security key on public networks.
WPA2-PSK is a good choice for home networks since it does not require an enterprise authentication server. But this standard has its drawbacks. Because it relies on a single passphrase for all clients, it may be less secure on larger networks. While AES is more secure, it also consumes more computing power, reducing productivity in the office. For example, a WEP network can only provide a transfer rate of 54 Mbps. WPA2-PSK uses the same encryption method.
WPA3 uses WPA2
WPA3 security does not require shared passwords. Instead, new devices are signed onto the network through processes without a shared password. One of these processes, known as Wi-Fi Device Provisioning Protocol, uses NFC tags or QR codes to authenticate devices and access the network. To do this, the device must first take a photo of a QR code or receive a radio signal.
The Wi-Fi Alliance announced the technical details for WPA3 in early 2018. The press release listed four major features: a more secure handshake, an easier way to add new devices, basic protection for open hotspots, and increased key size. These features are not mandatory, however, and only some manufacturers will implement them. Regardless of the changes, the network security key remains the same, which means that existing WPA2 devices will still work just fine with WPA3.
WEP uses 40-bit key
WEP, or Wide Area Encryption Protocol, is a network security standard that uses a 40-bit key and a 24-bit initialization vector to encrypt network traffic. When it was originally ratified by the IEEE in 1999, WEP used a weaker implementation of the RC4 Stream Cipher to encrypt data. While this encryption scheme initially supported keys of 40 bits and 64 bits, later implementations of the protocol could use 104-bit keys and a twenty-four-bit initialization vector.
Although WEP has many flaws, it’s still better than no security at all. The weakness of WEP’s encryption key allows an intruder to steal the key and gain access to an active Wi-Fi network. The emergence of more advanced encryption standards like WPA have mitigated WEP’s weaknesses and made it a better option for wireless network security. But what’s the best replacement for WEP?